Introduction
Blockchain technology is an innovative peer-to-peer transaction asset management system consisting of a tamper-proof database of transactions consistent across a large number of nodes, without an intermediary. Assets can be tangible or intangible such as intellectual property. At its center, a blockchain is a record of transactions with each computer node in the network holding a copy of the ledger, so there is no single point of failure. All new transactional data is encrypted and added as a new “block” to the chain of blockchain ledger historical records.
Blockchain transactions facilitate the movement of money, goods or secure data, a purchase at a mall shop, or the assignment of a citizen passport.
There are different categories of blockchain, defined by the participating stakeholders, including:
- Public – Permissionless: access to transactions are public, and no permissions are required to join. Bitcoin is an example.
- Private – Designated: access to the blockchain is limited to designated members.
- Hybrid of Public & Private / Sidechain: allows different, public or private blockchains to communicate with each other.
A network of nodes verifies transactions and recorded in a public distributed ledger called Blockchain. Every transaction is time-stamped and becomes part of a long chain / permanent record, and unable to be tampered with after set-up. The shared, distributed ledger records are an immutable history of all asset transactions between participants in the network and catalogs the current state of those assets. The business rules that govern blockchain transactions are agreed upon by all contracted members and encapsulated in chain-code, also known as smart contracts.
Unlike financial services providers that facilitate transactions with traditional national currencies, Blockchain supports the free transfer of cryptocurrency through a decentralized environment. All associated transaction data held in an interlinked network of computers, owned and operating by users.

Christian Catalini, MIT Sloan Assistant Professor: Blockchain Quote:
“At a high level, blockchain technology allows a network of computers to agree at regular intervals on the true state of a distributed ledger,” says an expert in blockchain technologies and cryptocurrency. “Such ledgers can contain different types of shared data, such as transaction records, attributes of transactions, credentials, or other pieces of information. The ledger is often secured through a clever mix of cryptography and game theory and does not require trusted nodes like traditional networks. This is what allows bitcoin to transfer value across the globe without resorting to traditional intermediaries such as banks.”
Blockchain & Bitcoin: Differences
It is essential to understand that cryptocurrencies are not the same as blockchain. As an analogy, view blockchain as a type of operating system, like Linux or Unix, that can run an array of applications and bitcoin is just one of many applications that can operate on a blockchain framework.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a type of unregulated digital currency created to bypass government currency controls and systems, simplify online transactions, and decrease transaction time, by eliminating third-party payment processing intermediaries.
Blockchain
Blockchain is the underpinning technology that maintains a Bitcoin and other types of the transaction ledger.
Blockchain is not only the supporting technology for cryptocurrency but has found full acceptance in the more traditional financial services industry and smart contracts.
Blockchain: Origin
Satoshi Nakamoto first revealed the Blockchain technology in his paper “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” which articulated the mathematical foundation and approach for bitcoin cryptocurrency.
“Online, we still can’t reliably establish one another’s identities or trust one another to transact and exchange money without validation from a third party like a bank or a government. These same intermediaries collect our data and invade our privacy for commercial gain and national security. Even with”
Don Tapscott, Blockchain Revolution: How the Technology Behind Bitcoin Is Changing Money, Business and the World
Blockchain: Business Uses
Blockchain technology is more promising than the cryptocurrency it was designed to support. The benefits of blockchain have the potential to sustain its value for the long-term to support an array of business transactions that encompass:
- Accounting
- Cash-Equity Trading
- Citizen Voting
- Civil Registry & Identity Records
- Drug Supply Chain
- Financial and Investment
- Food safety and Origin
- Insurance-Claim Payout
- Internet of Things – IoT
- Land Title
- New Music Releases
- Patents
- Peer-to-Peer Global Transactions
- Quality Assurance
- Smart Contracts
- Supply Chain Management
As Blockchain technology increases transactional trust and transparency across value chains, organizations will be empowered to innovate, collaborate, and compete in ways that provide a competitive advantage.
Blockchain: The New Technology of Change
“It’s a transformation that’s already begun. And organizations—both the ones that it can help, and the middlemen at risk of disintermediation —will need to be prepared as the technology matures.”
Goldman Sachs
Blockchain & IoT: Convergence
The convergence of Blockchain and IoT technologies epitomizes the prime technological disruption since the integration of computing and digital transaction processing systems. Due to continual high-velocity progress in device innovation and software, it is now possible to offer transaction processing and intelligence to digital devices everywhere 24/7. However, there are critical adaptability challenges associated with distributed systems, as well as security, coordination, intellectual property management, identity, and privacy.
Integrated Blockchain and IoT solutions can be created to support cryptographically secured data records protected against unauthorized alteration and modification. These solutions can be set-up to ensure trust, accountability, and transparency while streamlining business processing and reporting.
Internet of Things (IoT) enables a large number of devices to send data to private Blockchain ledgers for inclusion in shared transactions with secure and tamper-resistant records. The distributed replication blockchain enables organizations to access and supply IoT data without the need for central control and management. All business stakeholders can verify their transactions, preventing disputes, and ensuring each Blockchain partner is held fully-accountable for approved roles in the overall operation.
Blockchain can effectively stabilize the performance of multi-dimensional and complex IoT systems, thus safeguarding data safety and authenticity by quickly and safely storing protocols and various digital device results in a decentralized system. The distributed architecture of Blockchain allows for higher security: Even if network devices become hacked, it will not affect the performance of the total operation.
Dan Bieler – Analyst at Forrester: Blockchain – IoT Quote:
“it’s only normal that the distributed ledger technology, which blockchain is, will play a role in how devices will communicate directly between each other and keeping a ledger and thus trail of not just devices but also how they interact and, potentially, in which state they are and how they are ‘handled’ in the case of tagged goods.”
Organizations can use Blockchain – IoT solutions to manage data from edge devices—RFID-based assets, barcode, QR code scan events, and device data. These solutions can improve supply chains by tracking items as they navigate the import store network while authorizing delivery and credit extension. Blockchain innovation empowers secure traceability of confirmations and other notable data in supply chains.
Gartner’s 2018 CIO Survey reported:
43% have Blockchain on their radar but no planned actions to use it.
34% with interest in Blockchain.
1% with Blockchain adoption.
8% in short-term Blockchain planning or active experimentation.
14% engaged in Blockchain medium or long-term planning.
Blockchain & IoT: Benefits
Blockchain has the potential to significantly impact and change the manner that people buy and sell, interact with governmental agencies, and verify the legitimacy of everything in their business and social universes. In summary, blockchain combines the openness of the internet with the high-security of cryptography to provide a more convenient and safer means to verify critical data and establish trust.
Blockchain & IoT benefits as reported by IBM:
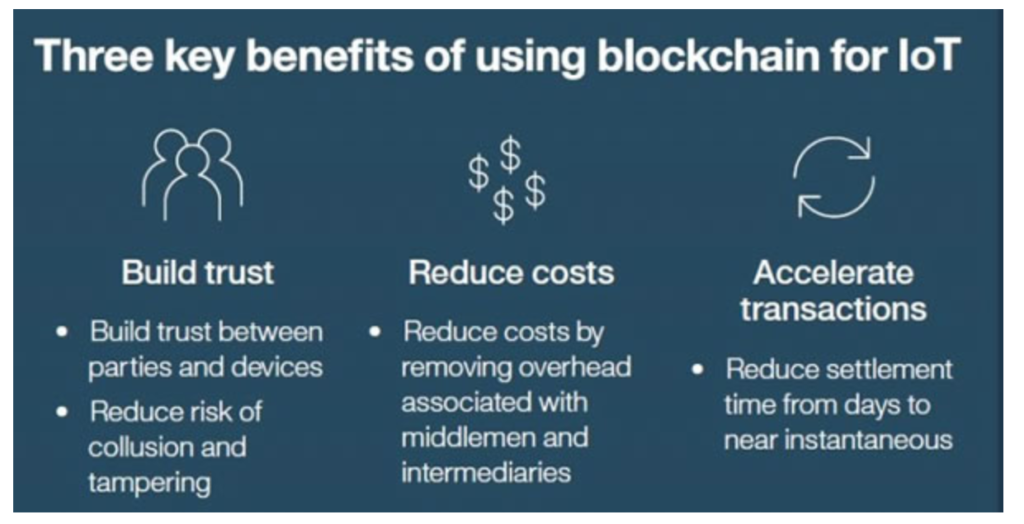
Programmable Economy & Monetization
According to Gartner:
‘Success with IoT will only be achieved via the development of a new economic platform and monetary operating model. Monetized ‘things’ will, therefore, redefine the economy.”
The ‘programmable economy,’ as predicted by most industry technology analysts. Based on the combination of “smart” technologies and distributed computing resources will significantly contribute to a successful transformation of the global economic system with new value exchange and new types of markets supported by the successful integration of Blockchain and IoT technologies.


