Introduction
Today, it is a reality that Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Cognitive Technologies can successfully emulate and supplement the power and processing of the human brain. This is a significant and valuable development for both the private and public sectors which have new and innovative opportunities to leverage and exploit the enormous amount of data pulsing through their organizations, and connected markets, governmental agencies, and individuals. Traditional computer technology has proven that it is not capable of effectively and efficiently extracting, evaluating, repurposing, and monetizing the massive amounts of structured and unstructured data.

AI technical concepts have been around for many decades, but we have only recently brought and applied sufficient computation power and data to power AI to make it acceptable for use with massive amounts of data. Technological advances in AI promise to be pervasive, with impacts and ramifications in health, economics, security, and governance. Opening up access to all private and public sector organizations could create a new trajectory for future economic growth.
Currently, computer power is significantly growing, algorithms and AI solutions are becoming more sophisticated, and the public and public sectors are generating once-unimaginable volumes of the data. Daily, billions of gigabytes are collected by networked devices ranging from web browsers to turbine sensors.
“Some people call this artificial intelligence, but the reality is this technology will enhance us. So instead of artificial intelligence, I think we’ll augment our intelligence.”
Ginni Rometty
AI is now transforming business and government in ways we’ve not seen since the Industrial Revolution; fundamentally reinventing how the organization, governmental entities, and markets, operate, interact, compete and prosper. When implemented holistically, these AI – cognitive technologies will meaningfully improve productivity and lower operating costs, unlocking more creative knowledge worker type jobs and creating new growth opportunities. In summary, AI is positioned to disrupt our world in a positive manner!
The terms Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cognitive Technologies are typically used interchangeably. Both reference technologies with the capability to perform and/or augment tasks, improve decision-making, and create interactions that have traditionally required substantial human intelligence, such as planning, reasoning from partial or uncertain information, and learning. The dawn of the cognitive era creates newer, more creative, and increased opportunities for organizations to generate value from their massive mountains data, in tandem with analytics advances.
McKinsey reports:
“Deployment of AI and automation technologies can do much to lift the global economy and increase global prosperity, at a time when aging and falling birth rates are acting as a drag on growth. Labor productivity growth, a key driver of economic growth, has slowed in many economies, dropping to an average of 0.5 percent in 2010–2014 from 2.4 percent a decade earlier in the United States and major European economies, in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis after a previous productivity boom had waned.
AI and automation have the potential to reverse that decline: productivity growth could potentially reach 2 percent annually over the next decade, with 60 percent of this increase from digital opportunities.”
Artificial Intelligence Definition
Artificial Intelligence (AI), to most people, still sounds more like something from an Avengers movie, however, it is increasingly real, and critical to the success of digital transformation environment. The demystification AI starts with the definition as outlined below.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines, to perform cognitive functions versus the natural intelligence (NI) displayed by humans. This includes: perceiving, reasoning, learning, interacting with the environment, solving problems, and exercising creativity.
Further, AI is a collection of advanced technologies that allows machines to sense, comprehend, act and learn. Colloquially, the term artificial intelligence is when a machine mimics cognitive functions that humans associate with other human minds, such as learning and problem solving.
AI technologies are significantly transforming the nature and context of how workers are being positioned in the emerging 100% digital workplace. This is witnessed by how smart equipment is continually replacing work activities traditionally completed by humans with positive quantifiable productivity and profitability outcomes. Cognitive technologies are products of the field of AI that perform tasks that only humans used to be able to do as follows:
- Computer Vision
- Deep Learning
- Intelligent Bots
- Machine Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- Physical Robots
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Rules-based Systems
- Speech Recognition
These new technologies are doing much more than just eliminating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes; they are supporting humans in completing complex and creative problem-solving activities by enabling an analysis of dauntingly vast amounts of data and identification of acts and trends previously impossible to discover and take timely decisions.
“The biggest risk is not taking any risk… In a world that changing really quickly, the only strategy that is guaranteed to fail is not taking risks.”
Mark Zuckerberg
Current Stages of AI Adoption Strategy
Gartner canvassed 83 members of its Research Circle in 2017 to identify where they stand on AI projects with the results presented below.
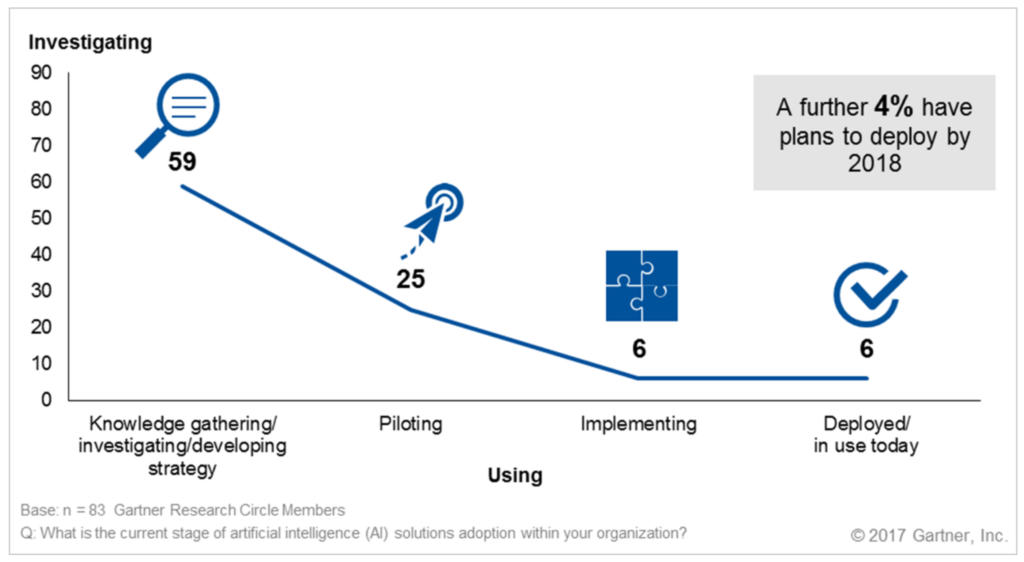
AI Topical Research
McKinsey, 2019 reported:
“We estimate AI-powered applications will add $13 trillion in value to the global economy in the coming decade, and leaders are energizing their agendas and investing handsomely in AI to capitalize on the opportunity—to the tune of $26 billion to $39 billion in 2016 alone.”
KM World 2018 reported:
“There may be a lot of hype about cognitive computing and artificial intelligence (AI), but the numbers back up the optimism. IDC reported that spending in that market reached $12 billion in 2017, an increase of nearly 60 percent over 2016. Predictions for the next four years are equally strong, with a slightly lower annual growth rate over that period but larger total market sizes. IDC predicts that by 2021, worldwide spending will reach $57.6 billion, reflecting an annual growth rate of about 50 percent. Retail and banking will lead the market in dollars spent, with manufacturing and healthcare following.”
McKinsey Global Institute in 2017 reported:
‘That rapid advances in automation and artificial intelligence will have a significant impact on the way we work and workplace productivity. To successfully create value in this emerging market, organizations are experimenting with different strategies, technologies, and opportunities, all of which require large financial and human resource investments.”
AI-Enabled Business
In the current environment, we have organizations with labels as ‘Internet Companies.’ The fundamental concept that defines an Internet Company is whether the organization has successfully created and implemented the underlying business model that fully leverages and exploits the innovative value-add capabilities of the Internet.
With the emergence and widespread business acceptance of AI technology, companies who desire to be regarded as ‘AI Companies’ will need to rearchitect their businesses to take total advantage of AI technology. Just as deploying a website doesn’t make a business an Internet Company, the modest use of AI supporting technology solutions will not earn the title of AI Company.
Future AI Industry Use – McKinsey 3 Years Projection
McKinsey, in 2018, reported that AI technologies have the potential to create $3.5 – $5.8 trillion in value annually across business functions in the industry sectors shown in the below McKinsey graphic.
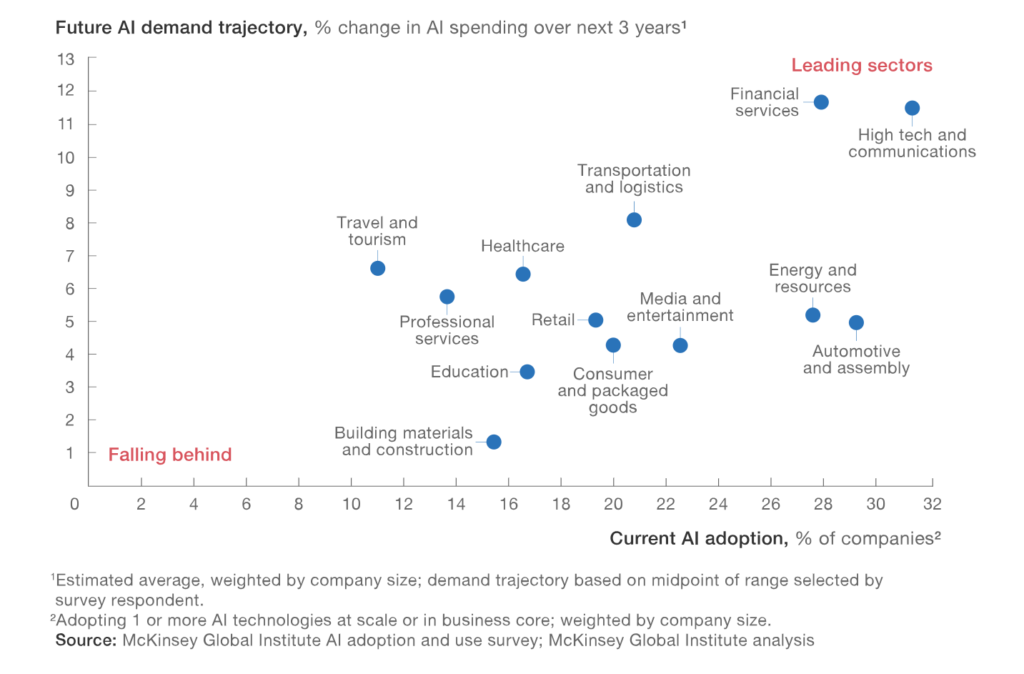
AI Benefits
Research shows that AI is already transforming how organizations do business, manage customer, patient, and citizen relationships and fuel groundbreaking innovation. Key benefits realized by the successful deployment of AI-supported solutions include:
- Automate routine work activities.
- Avoid mistakes and ‘human error’.
- Enable more timely business decisions with outputs from cognitive technologies.
- Enhance process efficiency and throughput.
- Free-up humans to do what they do best.
- Generate business and market insights.
- Improve learning and knowledge-building.
- Improve regulatory compliance.
- Reduce operational costs.
- Reduce false positives.
While it is important to recognize and understand AI benefits to drive adoption, it is equally vital for decision-makers to consider data security and privacy, data quality, and potential issues of bias for AI-based solutions intended for deployment.
“Computers won’t replace human, technology will allow humans to be human”
Carrie Schwab Pomerantz
AI, Data Governance & Quality
AI solution performance, in an organizational setting, is largely contingent on the state of data governance and quality of corporate data. Organizations that value and conduct a data cleansing project prior to AI deployment have a higher percentage probability for success and realization of planned benefits.
For example, systems with recognized levels of data duplication, incomplete information, improperly formatted data sets, and data points that aren’t necessary for core business processes, will undoubtedly prove to be impediments for AI solutions to effectually: discover, computer, and generate high-probability insights, information responses, and decision-making.
“Many enterprises still treat AI as a software program, a tool. No one would expect a tool to “act” responsibly, explain its decisions, or work well with others. But with AI systems making decisions that affect people, companies must teach AI to do all of these things and more. After all, with great power comes great responsibility.
We call it “Citizen AI”.
Accenture
Best-in-Class AI Use: Examples
As organizations continue their acceptance of digitization, they’re increasingly adding AI solutions to their value-creation toolboxes. Examples of successful AI solution use within the private and public-sector community include:
Financial Industry: use automated fraud detection and machine learning to identify human and transactional behavior patterns; use speech recognition to automate customer service telephone communications and interactions.
Healthcare Industry: use systematized speech recognition to transcribe physician-patient notes and official documents; use computer vision to automate mammograms and other body condition image analysis; automate reading and comprehending the huge amounts of the medical literature; automate hypothesis generation techniques for diagnosis and machine learning.
High-Technology Industry: use automated computer vision and machine learning to enhance computer and system products and create new products and services.
Life Sciences Industry: use systematize machine learning systems to predict biological data and compound activity cause-and-effect relationships to identify new advanced or repurposed pharmaceuticals.
Media and Entertainment Industry: use automated data analytics and natural language generation to automate create media and supporting narrative material.
Public Sector: use cognitive technologies to support governmental regulations, rules, and processes for surveillance, compliance and fraud detection.
Retail Industry: use automated machine learning to discover attractive cross-sell and up-sell offers and effective incentive-based promotions.
Gartner reported in 2017 AI Research:
“What makes the best AI projects stand out is that they allow for solutions that previously would have been impossible to conceive, because they include what seems like human insights but at a volume humans could never achieve.”


